Libusb.org USB Devices Driver Download For Windows
libusb-win32 is a port of the USB library libusb 0.1 (http://sourceforge.net/projects/libusb) to the Microsoft Windows operating systems (Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7; Windows 98 SE and Windows ME for versions up to 0.1.12.2 ). The library allows user space applications to access many USB device on Windows in a generic way without writing any line of kernel driver code.
Vista/7/2008/2008R2 64 bit are supported from version 1.2.0.0 since a Microsoft KMCS accepted digital signature is embedded in the kernel driver libusb0.sys.
Release Notes
Libusb Usb Device Driver Download For Windows 7
Select Update Driver. If Windows doesn't find a new driver, you can try looking for one on the device manufacturer's website and follow their instructions. Reinstall the device driver. In the search box on the taskbar, enter device manager, then select Device Manager. Right-click (or press and hold) the name of the device, and select Uninstall. Signed Driver USB VCOM STB Android B760h (Mediatek), B860h (Amlogic) Untuk menghubungkan perangkat STB Android B760h, B860h (chipset Amlogic/mediatek) ke Windows 7/8/10 melalui USB dibutuhkan driver libusb-win32 worldcupdevice, atau MediaTek Preloader USB VCOM akan tetapi sertifikat asli dari driver ini sudah kadaluwarsa sehingga saat menginstallnya kita akan menemukan peringatan seperti. When you plug the device into your USB, Windows will look for the associated driver, if it cannot find this driver then you will be prompted to insert the driver disc that came with your device. Common USB Device errors are ‘ usb port not working ‘, ‘device descriptor request failed error’ or ‘bugcodeusbdriver’ issues.
Dependencies
This package has no dependencies.
Used By
NuGet packages
This package is not used by any NuGet packages.
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
Version History
| Version | Downloads | Last updated |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2.6 | 2,431 | 6/6/2016 |
| 1.2.5 | 562 | 6/6/2016 |
| 1.2.4 | 537 | 6/6/2016 |
| 1.2.3 | 483 | 6/6/2016 |
| 1.2.2 | 506 | 6/6/2016 |
| 1.2.1 | 578 | 6/6/2016 |
- 1Using flashrom on Windows
- 2Building flashrom on Windows using MinGW/MSYS.
- 2.1Requirements
Requirements
In order to use flashrom on Windows you must either build it from source as explained below or just download a snapshot from here.If your programmer is COM or LPT-based, there is nothing more to do, because Windows has all drivers needed.
It isn't so easy for USB-based devices, because they needed a special libusb-win32 driver, that must be generated and installed to make it available to the flashrom executable.Because the nature of the generation process, the driver has no digital signature and can't be installed on 64-bit Windows versions without some preparations.
Obtaining libusb-win32
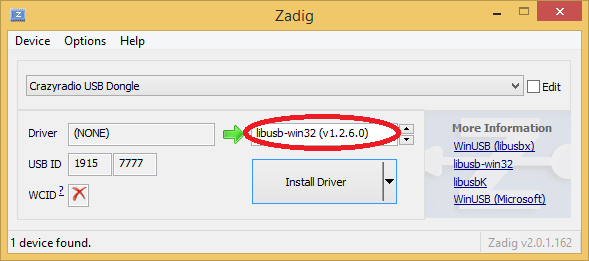
The required installation file can be found on the libusb-win32 project site.Please use the same version that was used for flashrom compilation as indicated by the download path.
Download the file named libusb-win32-bin-x.y.z.t.zip and unpack /libusb-win32-bin-x.y.z.t/bin directory from it.
Making libusb-based driver for your device
- Attach your USB device and click on Cancel or Close on the Driver Installation Wizard window.
- Run inf-wizard.exe from the unpacked bin directory. Click on Next.
- Select your device from the list, click on Next.
- Do not alter Vendor ID, Product ID and MI. You can alter Manufacturer and Device names, if you want. Click on Next.
- Select the destination for the newly created driver and click on Save.
- If you are using 32bit Windows version or 64bit Windows version with unsigned driver installation option enabled, click on Install Now... to install the driver.
- If you receive an error message instead of a successful driver installation, disable the enforced driver signing (your favorite search engine will give you details about that) and install the driver after that.
- Detach your device and attach it once again to finish the installation.
Using flashrom
After installing the drivers successfully you can use flashrom without Administrator privileges.Consult the man page about how to use it in general and the options available for your programmer.
Before you set up a MinGW/MSYS build environment, note that you may find usable Windows binaries in our buildbot archive. However, they are usually untested and not recommended to be trusted blindly.
Requirements
MinGW/MSYS
In order to build flashrom and various of its dependencies, we need a UNIX-like environment on Windows, which is provided by MinGW/MSYS.
- Download the latest version (20110530 currently) of the automated MinGW installer named mingw-get-inst (double-click the installer *.exe, which will download and install all components).
- Make sure you enable 'MinGW Compiler Suite', 'C++ compiler', 'MSYS Basic System', and 'MinGW Developer Toolkit' in the installer.
- For simplicity it's recommended to leave the default install location of c:MinGW unchanged.

Now open a MinGW shell via Start/Programs/MinGW/MinGW Shell and do the following:
- Additionally, pkg-config is needed. There are a few ways to do this. The MinGW FAQ has some suggestions: Extract the binary from GTK or use an alternative implementation. A flashrom user describes the steps for extracting pkg-config from GTK in this issue on Github.
If you are using MSYS2, pacman can also be used:
libusb-win32
- Download and execute libusb-win32-devel-filter-1.2.6.0.exe.
- Download and extract libusb-win32-bin-1.2.6.0.zip.
- Copy lusb0_usb.h to (the equivalent of) /usr/local/include.
libftdi
- Install libftdi. The easiest method is probably to use the libftdi-0.18_mingw32.zip binaries from here.
- Extract the ZIP file into a temporary directory.
- Copy dll/libftdi.dll to /usr/local/bin.
- Copy lib/libftdi.a and lib/libftdi.dll.a to /usr/local/lib.
- Copy include/ftdi.h to /usr/local/include.
Building flashrom
Checkout the flashrom source code (see the download page for instructions), then:
First you need to install MinGW (on Ubuntu it is enough to install the package mingw32).Of course all the normal build utilities are needed like make etc. (usually contained in a package named build-essential or similar).If you want to use libusb or libftdi you need to get the headers and static library files (*.a).The latter can either be downloaded pre-built or need to be (cross-)compiled.For libusb-win32 this even requires a Windows SDK which makes the whole point of cross-compiling a bit moot.See the respective source packages for documentation on how to cross-compile them.
Libusb.org USB Devices Driver Download For Windows
The headers and libraries should be organized in a Unix-like directory layout, i.e. a (sub) directory named 'lib' containing the static libraries (*.a), 'bin' with non-static libraries (*.dll) if need be, and 'include' with the headers (*.h).
You can then compile flashrom.exe with
A relative path (originating in the flashrom directory) is allowed as LIBS_BASE's value.The compiler to be used (given by the CC value) depends on the MinGW edition you are using.